A tender procedure has been published by the Asinara National Park
The tender procedure for the design service for new mooring systems for buoys within the "Isola dell'Asinara" Marine Protected Area foreseen in the action C3 has been published on the Public Administration Electronic Market (MePA).

The action C3 has the purpose of creating mooring areas in areas where the management plan does not provide for free anchoring and in any case to protect particularly sensitive areas characterized by anthropogenic pressure generated by the use of boats in the summer season. Therefore, eco-compatible moorings will be installed. In addition to the conservation of the Posidonia seabeds, therefore, their installation can also increase the possibility of use by boaters.
More results from the A1 action
Study of the wave climate, mapping of coastal sandy deposits and analysis of seismic/acoustic data for actions C2 and C3
Different activities were carried out under Action A1 from the beneficiary IAS-CNR to improve knowledge on envisaged areas of the SeaForest LIFE project. The studies were carried out to define wave climate and to update the seabed habitat maps. The seagrass meadow upper limit and coastal sandy deposits maps were updated through the interpretative analysis of available data, such as orthophotos, satellite images, seismic data, multibeam and backscatter.


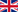
The analysis of the statistical characteristics of the synthetic parameters of the wave motion was performed to define the wave climate regimes of the marine sectors overlooking the study areas. To perform wave event and hydrodynamics simulations, to complete the marine climate, and to perform the most representative hydrodynamics scenarios generated by wave events, the software suite Delft3D was used.

The seabed mapping was a preparatory activity foreseen by action A1 and an implementation activity for C2 and C3 Actions. The definition of the upper limits of the Posidonia oceanica meadows, the identification of the coastal sandy deposits suitable to host the recreational nautical free berth and the supply of the database for the mooring planning are the objectives of these activities.

The acquisition and analysis of seismic lines were carried out to define the thicknesses of the sandy bodies, the thickness of Posidonia oceanica mattes and the detection of solid substrates. The results of the seismic analysis were useful to support the assessment of carbon storage, to improve the characterization of habitat 1120 and to support the management and design of anchors and moorings. The characterization of the study areas to realize the maps of the coastal habitats at a low depth, and the creation of the database to support the development of the mooring plan (Action C2-C3), where possible.
Here you can download the full report.

Collaboration with the Carabinieri Diving Unit of Naples
On 20 and 21 February, ISPRA researchers went to the Cilento, Vallo di Diano and Alburni National Park as part of the SeaForest LIFE project.
The first day they presented to the Park Director, Dr Romano Gregorio, the preliminary data on the census of boats present in summer in the two Marine Protected Areas present within the Park (the MPA of Santa Maria di Castellabate and the MA Costa degli Infreschi and della Masseta), at the Center for Studies and Research on Biodiversity in Vallo della Lucania (SA).
On 21 February an operational meeting was held with the Head of the Marine Protected Areas and Park Community Service, Dr Francesco De Luca, and the members of the Carabinieri Diving Unit of Naples, at Villa Matarazzo (Castellabate - SA). Thanks to this important meeting, a collaboration between the Carabinieri and SeaForest LIFE has started. The Carabinieri will guarantee technical and logistical support to ISPRA researchers for monitoring activities on Posidonia oceanica in the MPAs of the Cilento National Park. Thanks to the precious help that will be provided by the Carabinieri Diving Unit of Naples, our project will be able to collect important data to better quantify the precious carbon stored by the Posidonia oceanica meadows under the sea surface, so useful to mitigate, at least in part, the effect of climate change on our future.

Marini Pulcini, Sante Francesco Rende, Luca Parlagreco and Silvia Maltese participated for ISPRA, and the Mar. Magg. Sandro Buccalo (Comandante Aliquota Subacquei Napoli), the Mar. Magg. Santi Scolaro (Vice Comandante), and the Brig. Fabio Vitozzi, the Vice Brig. Gennaro Attore, the Vice Brig. Giovanni Falco (infermiere F. SUB), the App. Sc. Q.S. Salavatore Pantalena, the App. Sc. Marco Panico for the Carabinieri Diving Unit of Naples.
The first results of the SeaForest LIFE project are now available
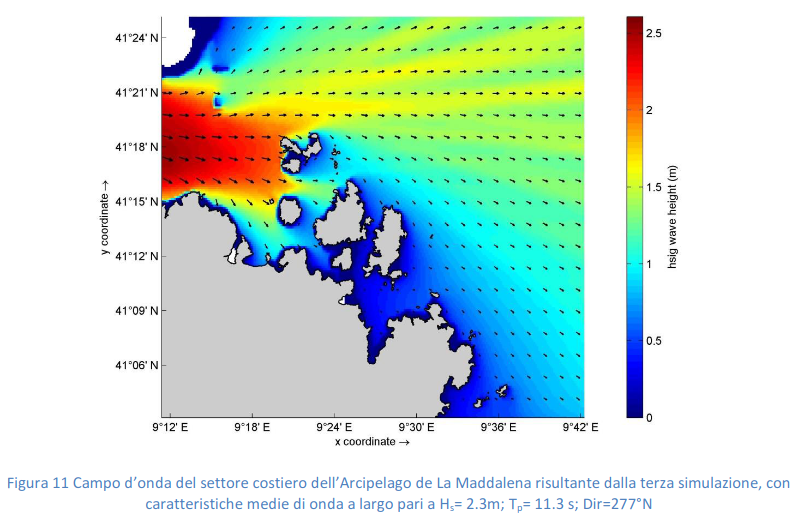
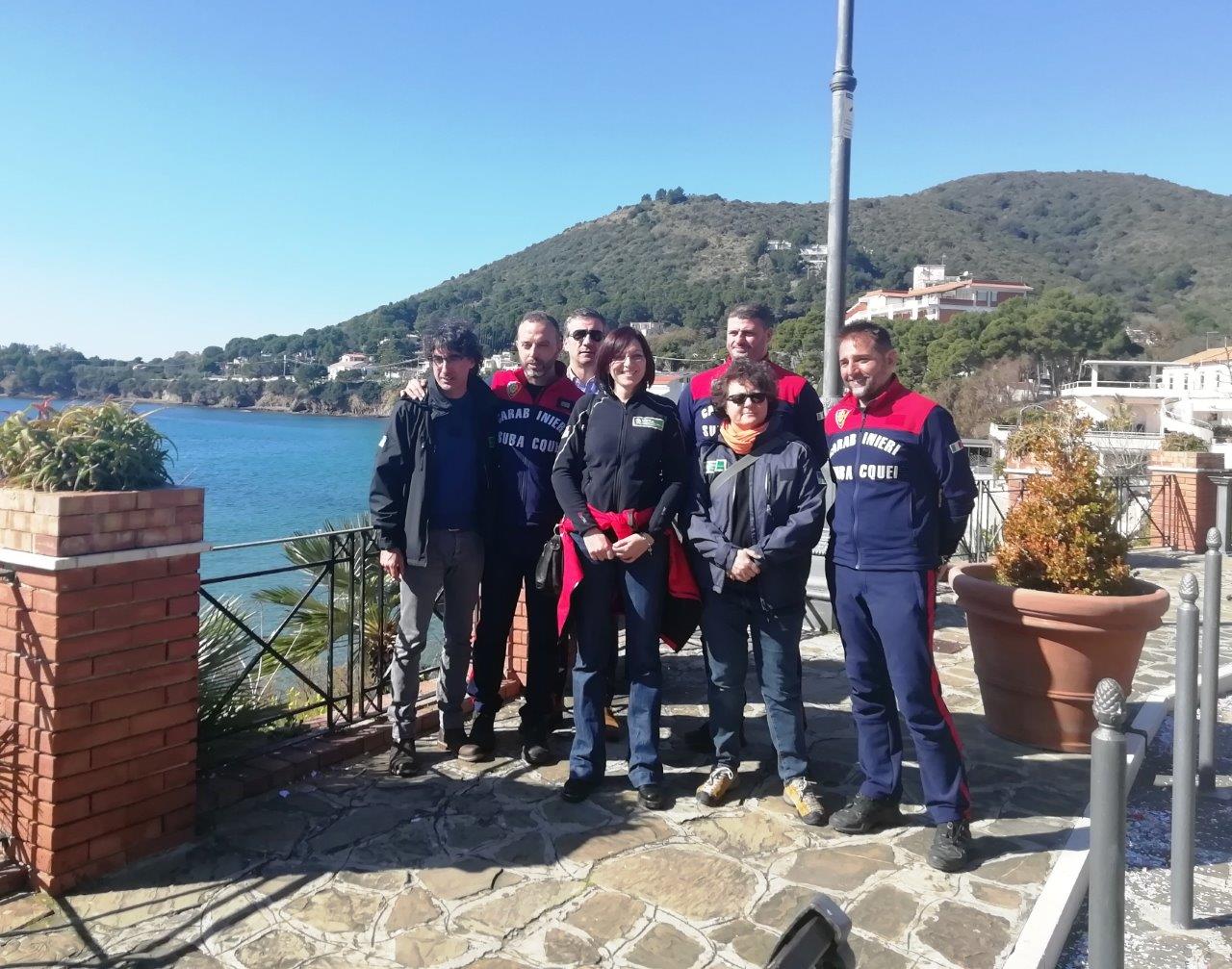
Under Action A1.1, the assessment of the extent of the habitat in the Blue Carbon study areas was carried out through the analysis of high-resolution and medium-resolution multispectral satellite images. Using the satellite images we could detect the presence and extent of seagrass meadows with different degrees of density and coverage (<25% to 100%) in the study areas. These systems, together with the in situ observations, represent powerful tools to map the extension of the Posidonia oceanica meadows minimizing the CO2 emissions related to the in situ survey activities. This Remote Sensing analysis activity was mainly performed by qualified ISPRA researchers, with the support of the external service of the University of Calabria Spin-off “3D Research”, which mainly dealt with the water column correction procedure. Maps of P. oceanica meadows in the Blue Carbon areas have been updated (from 1999 to 2019).
From the point of view of variations, slight reductions in the areas covered by P. oceanica were found in all Blue Carbon areas in the three National Parks (Parco Nazionale dell'Arcipelago di LaMaddalena, Parco Nazionale dell'Asinara, Parco Nazionale del Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni). In addition, for all the study areas, the information layers to estimate the carbon storage in P. oceanica have been prepared using the Invest Model (Natural Capital Project).

At the same time, a cartographic study has been carried out in order to quantify the pressure induced by the anchorage of pleasure boats on P. oceanica meadows in the investigated Blue Carbon areas. This survey was carried out using semiautomatic and automatic boat recognition procedures. The acquired data enabled us to quantify the level of pressure exerted by pleasure boating on the Blue Carbon P. oceanica habitat.
The preliminary results have pointed out that the investigated Blue Carbon areas represent, in the three National Parks, the most frequented areas for recreational boating. In these areas there are a lot of boats anchoring on P. oceanica habitat, leading to a foreseeable impact and degradation on the conservation status of the seagrass meadows with possible negative effects on the Blue Carbon production and CO2 storage capacity.

The full report has been uploaded to the Products section of our website and is available here.

ESP10 Hannover
Today, 24/10/2019, we presented our project at the 10th World Conference on Ecosystem Services organized by the Ecosystem Services Partnership in Hannover, Germany.
We have been invited and hosted at this great event by the LIFE communication stand and this is a source of great pride for us.
Our latest publication and the ecosystem services offered by Posidonia oceanica were at the center of the stand and disseminated to a large number of insiders from all over the world.